During a lightning flash there exists a potential difference of – During a lightning flash, a substantial potential difference manifests, creating a captivating phenomenon that has intrigued scientists and engineers for centuries. This electrical discharge not only illuminates the night sky but also carries significant implications for our understanding of atmospheric physics and its impact on our surroundings.
Lightning formation involves the accumulation of electrical charges within thunderclouds, leading to the development of a potential difference between the cloud and the ground. This difference in electrical potential drives the lightning strike, releasing immense energy in the form of a powerful electrical current.
Lightning Formation and Electrical Discharge: During A Lightning Flash There Exists A Potential Difference Of
Lightning is a powerful electrical discharge that occurs naturally in the atmosphere. It is caused by the buildup of electrical charges within clouds or between clouds and the ground. When the potential difference between these charged regions becomes sufficiently large, an electrical discharge occurs in the form of a lightning flash.
The process of lightning formation begins with the separation of electrical charges within a cloud. This separation can be caused by a variety of factors, including the collision of ice particles and the movement of air currents. As the charges separate, they create a region of positive charge and a region of negative charge within the cloud.
The positive charge typically accumulates at the top of the cloud, while the negative charge accumulates at the bottom.
If the potential difference between the positive and negative charge regions becomes large enough, an electrical discharge will occur. The path of the discharge is determined by the conductivity of the air between the charged regions. The air is typically a poor conductor of electricity, but it can become ionized when the potential difference is sufficiently high.
Once the air is ionized, it becomes a conductor of electricity, and the electrical discharge can travel through it.
The electrical discharge that occurs during a lightning flash can be extremely powerful. The current can reach tens of thousands of amperes, and the voltage can reach millions of volts. The energy released by a single lightning flash can be equivalent to the energy released by a small nuclear explosion.
Potential Difference
The potential difference between two points is a measure of the electrical potential energy difference between those points. It is measured in volts. The potential difference between the positive and negative charge regions within a cloud is what drives the electrical discharge that occurs during a lightning flash.
The potential difference between two points can be measured using a voltmeter. A voltmeter is a device that measures the difference in electrical potential between two points. Voltmeters are typically used to measure the voltage of batteries, power supplies, and other electrical devices.
Measurement and Observation of Potential Difference
The potential difference between the positive and negative charge regions within a cloud can be measured using a variety of techniques. One common technique is to use a lightning rod. A lightning rod is a metal rod that is placed on a tall structure, such as a building or a tree.
The lightning rod is connected to the ground with a wire. When lightning strikes the lightning rod, the electrical current flows through the wire and into the ground.
Another technique for measuring the potential difference between the positive and negative charge regions within a cloud is to use a balloon-borne instrument. A balloon-borne instrument is a device that is carried aloft by a balloon. The instrument is equipped with sensors that can measure the electrical potential at different altitudes.
The measurement of the potential difference between the positive and negative charge regions within a cloud can provide valuable information about the development of lightning. This information can be used to help predict when and where lightning is likely to strike.
Challenges and Limitations
There are a number of challenges and limitations associated with the measurement of the potential difference between the positive and negative charge regions within a cloud. One challenge is that the potential difference can change rapidly over time. This can make it difficult to get an accurate measurement.
Another challenge is that the potential difference can vary greatly from one location to another. This can make it difficult to get a representative measurement.
Despite these challenges, the measurement of the potential difference between the positive and negative charge regions within a cloud can provide valuable information about the development of lightning. This information can be used to help predict when and where lightning is likely to strike.
Magnitude and Variation of Potential Difference
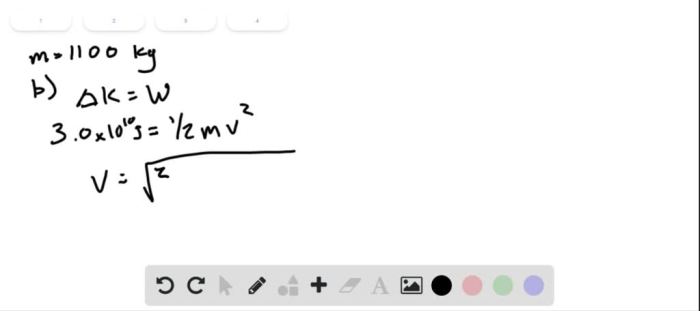
The potential difference between the positive and negative charge regions within a cloud can vary greatly. The typical potential difference is between 100 million and 1 billion volts. However, potential differences as high as 2 billion volts have been measured.
The potential difference between the positive and negative charge regions within a cloud can also vary over time. The potential difference typically increases as the lightning flash develops. The potential difference can reach its peak value just before the lightning flash occurs.
The potential difference between the positive and negative charge regions within a cloud can also vary from one location to another. The potential difference is typically higher near the center of the cloud than it is at the edges of the cloud.
Factors Influencing Variation, During a lightning flash there exists a potential difference of
There are a number of factors that can influence the variation in potential difference between the positive and negative charge regions within a cloud. These factors include:
- The size of the cloud
- The height of the cloud
- The temperature of the cloud
- The amount of moisture in the cloud
- The presence of ice particles in the cloud
Impact of Potential Difference on Surrounding Environment
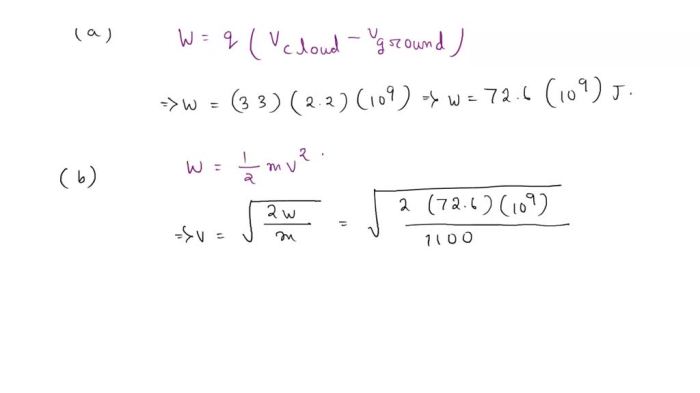
The potential difference between the positive and negative charge regions within a cloud can have a significant impact on the surrounding environment. The potential difference can cause the air around the cloud to become ionized. This can lead to the formation of lightning bolts.
The potential difference can also cause the ground beneath the cloud to become charged. This can lead to the formation of ground currents. Ground currents can be dangerous because they can cause electrical shocks.
The potential difference between the positive and negative charge regions within a cloud can also affect the weather. The potential difference can cause the air around the cloud to become warmer. This can lead to the formation of updrafts. Updrafts can cause the cloud to grow taller and wider.
Potential Hazards and Safety Considerations
Lightning strikes can be dangerous. They can cause serious injuries or even death. It is important to take precautions to avoid being struck by lightning. These precautions include:
- Staying indoors during thunderstorms
- Avoiding contact with metal objects
- Seeking shelter in a sturdy building or vehicle
Applications and Implications
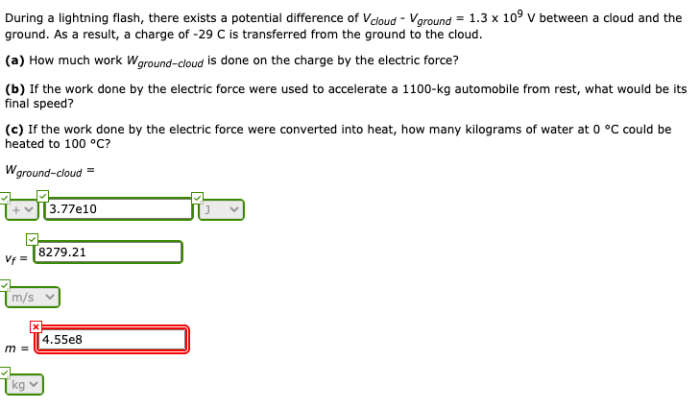
The knowledge of the potential difference between the positive and negative charge regions within a cloud has a number of applications. This knowledge can be used to:
- Predict when and where lightning is likely to strike
- Design lightning protection systems
- Develop early warning systems for lightning
The knowledge of the potential difference between the positive and negative charge regions within a cloud can also be used to improve our understanding of the atmosphere. This knowledge can help us to better predict the weather and to mitigate the effects of lightning strikes.
Potential Applications
Some potential applications of the knowledge of the potential difference between the positive and negative charge regions within a cloud include:
- The development of new lightning protection systems
- The development of early warning systems for lightning
- The improvement of weather forecasting
- The mitigation of the effects of lightning strikes
Question & Answer Hub
What causes the potential difference during a lightning flash?
The potential difference arises from the separation of electrical charges within thunderclouds, creating an imbalance between the cloud and the ground.
How is the potential difference measured?
Specialized instruments, such as electric field mills and lightning mapping arrays, are used to measure the potential difference during a lightning flash.
What factors influence the magnitude of the potential difference?
The distance from the lightning strike, the size of the thundercloud, and the atmospheric conditions can all affect the magnitude of the potential difference.
What are the safety considerations associated with lightning strikes?
Lightning strikes pose significant safety hazards. It is essential to seek shelter indoors or in a hard-top vehicle during thunderstorms and avoid open areas, tall structures, and bodies of water.