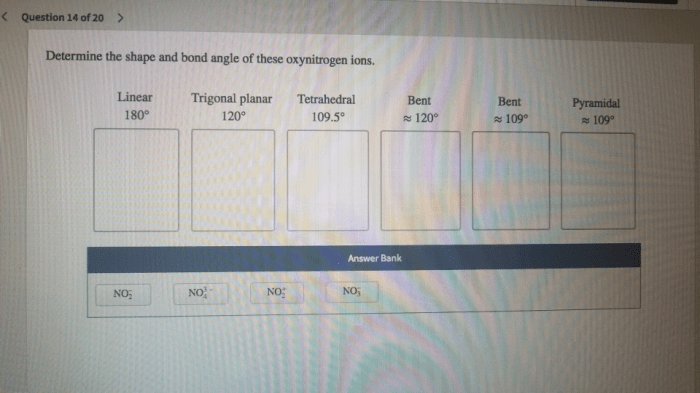
Determine the shape and bond angle of these oxynitrogen ions. – Embark on an enthralling exploration of oxynitrogen ions, where we unravel the intricate relationship between molecular geometry and bond angles. Delving into the realm of VSEPR theory, we uncover the factors that shape these ions’ unique structures and delve into the hybridization of the nitrogen atom, revealing its profound impact on molecular geometry and bond angles.
Prepare to be captivated as we unveil the secrets of these fascinating ions, providing a comprehensive understanding of their diverse characteristics.
Determine the Shape and Bond Angle of Oxynitrogen Ions: Determine The Shape And Bond Angle Of These Oxynitrogen Ions.
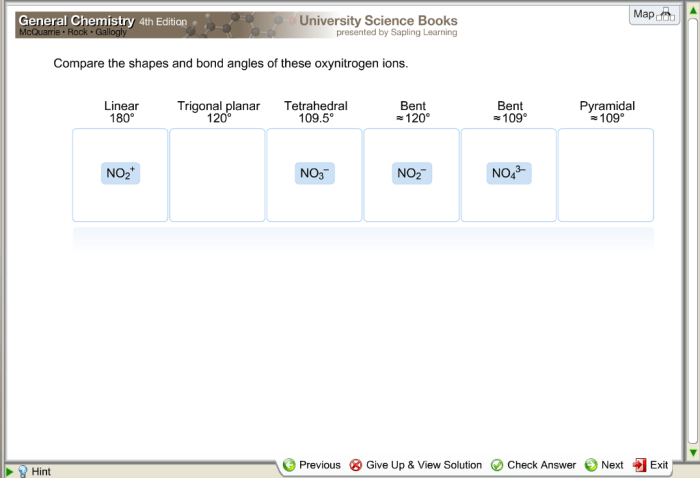
Oxynitrogen ions are polyatomic ions that contain both nitrogen and oxygen atoms. They are formed when an oxygen atom bonds with a nitrogen atom and share electrons. The shape and bond angle of oxynitrogen ions can vary depending on the number of atoms and the type of bonds involved.
Lewis Structure
The Lewis structure of an oxynitrogen ion shows the arrangement of atoms and the distribution of electrons in the molecule. To draw the Lewis structure, we first need to determine the total number of valence electrons in the ion. For example, the nitrite ion (NO 2–) has a total of 18 valence electrons (5 from nitrogen, 6 from each oxygen, and 1 extra electron for the negative charge).
The Lewis structure of the nitrite ion is shown below:
“`:O::N(:O:) –“`
In this structure, the nitrogen atom is bonded to two oxygen atoms by double bonds. The nitrogen atom also has one lone pair of electrons.
Molecular Geometry, Determine the shape and bond angle of these oxynitrogen ions.
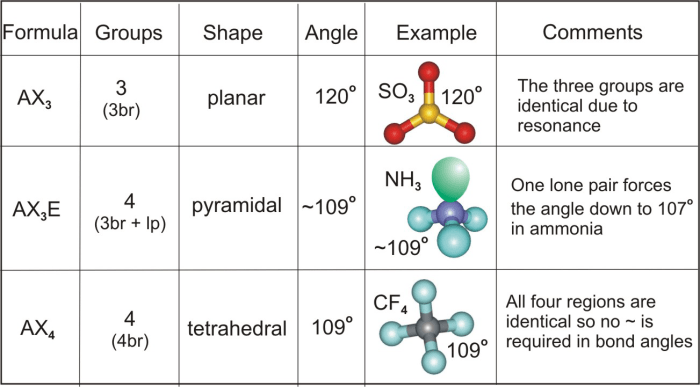
The molecular geometry of an oxynitrogen ion is determined by the number of electron pairs around the central atom. According to VSEPR theory, the electron pairs will arrange themselves in a way that minimizes repulsion between them.
For example, the nitrite ion has three electron pairs around the nitrogen atom: two bonding pairs and one lone pair. According to VSEPR theory, these electron pairs will arrange themselves in a trigonal planar geometry.
Bond Angle
The bond angle in an oxynitrogen ion is the angle between the two bonds to the central atom. The bond angle is determined by the molecular geometry of the ion.
For example, the nitrite ion has a trigonal planar molecular geometry. This means that the bond angle between the two N-O bonds is 120 degrees.
Hybridization
The hybridization of an atom refers to the mixing of atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals. The type of hybridization that occurs depends on the number of electron pairs around the atom.
For example, the nitrogen atom in the nitrite ion has three electron pairs around it. This means that the nitrogen atom is sp 2hybridized. The sp 2hybridization results in the formation of three hybrid orbitals that are arranged in a trigonal planar geometry.
Examples
There are many different types of oxynitrogen ions. Some examples include:
- Nitrite ion (NO 2–): trigonal planar, 120-degree bond angle
- Nitrate ion (NO 3–): trigonal planar, 120-degree bond angle
- Nitrous oxide (N 2O): linear, 180-degree bond angle
- Nitrogen dioxide (NO 2): bent, 134-degree bond angle
The shape and bond angle of oxynitrogen ions can vary depending on the number of atoms and the type of bonds involved.
Common Queries
What is the significance of determining the shape and bond angle of oxynitrogen ions?
Understanding the shape and bond angles of oxynitrogen ions is crucial for predicting their reactivity, stability, and physical properties. It enables researchers to tailor these ions for specific applications, such as catalysis, materials science, and pharmaceutical development.